As one of the top China cardboard tube packaging manufacturers and paper tube packaging suppliers, we devote all of our efforts to research and launch more high quality packaging products to global market.
Cardboard tubes, also commonly referred to as paper tubes, cores, or mailing tubes, are versatile cylindrical structures manufactured from layers of paperboard, kraft paper, or other fibrous materials. Their construction involves a precise winding process that results in a lightweight yet robust product with a high strength-to-weight ratio.
Manufacturing Processes
The production of cardboard tubes is a highly engineered process, with two primary methods dominating the industry:
-
Spiral Winding: This is the most common and efficient method for producing long, continuous tubes. Thin strips of paper, coated with an adhesive, are fed at an angle onto a rotating mandrel. As the mandrel spins, the paper strips are wound in a continuous spiral, building up layers to achieve the desired wall thickness and strength. This process is ideal for creating tubes of uniform diameter and a seamless inner surface, which is crucial for applications like industrial cores. The angle of the wind and the tension applied during the process are critical factors that determine the final tube's crush strength and stiffness.
-
Convolute Winding: In this method, a full-width sheet of paper or paperboard is wrapped around a mandrel in a parallel fashion, with each successive layer applied directly over the previous one. This creates a tube with a visible seam that runs parallel to its length. Convolute winding is often used for producing thicker-walled tubes or those with specific dimensional requirements, as it allows for greater precision in wall thickness and is better suited for producing tubes of a shorter length and a larger diameter.
Material Composition and Properties
The properties of a cardboard tube are directly influenced by the materials used in its construction. Key materials include:
-
Kraft Paper: Known for its high tensile strength and durability, kraft paper is a primary component, providing the core structural integrity of the tube.
-
Recycled Paperboard: Using recycled materials is a cornerstone of sustainable manufacturing. Recycled paperboard is a common filler material that contributes to the tube's thickness and rigidity.
-
Adhesives: Water-based or hot-melt adhesives are used to bond the paper layers together. The type of adhesive affects the tube's moisture resistance and heat tolerance.
The key properties that can be engineered in a cardboard tube include:
-
Wall Thickness: Ranging from a few millimeters to several centimeters, wall thickness directly correlates with the tube's crush strength and rigidity.
-
Crush Strength: This is a critical metric that measures the tube's ability to withstand compressive forces, either from the sides (flat crush) or from the ends (axial crush). This property is vital for applications where the tube must support heavy loads or resist crushing during stacking and shipping.
-
Inner Diameter (ID) and Outer Diameter (OD): These dimensions are specified to meet the precise needs of a given application, from a small core for a roll of tape to a large form for a concrete column.
-
Moisture Resistance: Specialized coatings or adhesives can be applied to enhance the tube's resistance to humidity and moisture, protecting its integrity in various environments.
Diverse Applications Across Industries
The versatility of cardboard tubes has made them an indispensable component in a wide array of industries:
-
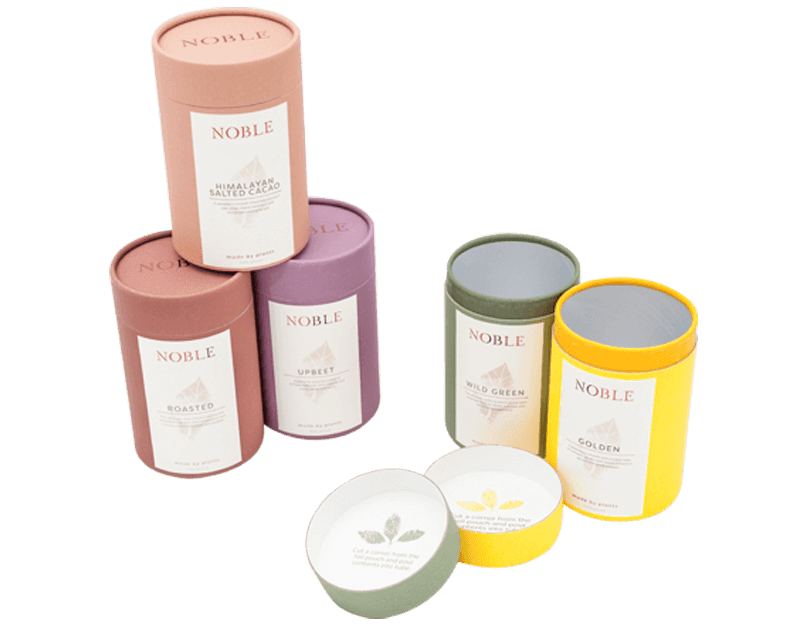
Packaging and Shipping: This is perhaps their most recognizable use. Mailing tubes are essential for protecting rolled documents, posters, art, and blueprints from creasing and damage during transit. For commercial goods, custom tubes with printed labels and closures are used for packaging snacks, cosmetics, and spirits, offering a premium and eco-friendly alternative to plastic containers.
-
Industrial Cores and Winders: In manufacturing, tubes serve as cores for winding materials into large rolls. This includes everything from paper towels and toilet paper to textiles, plastic films, labels, and metal foil. The dimensional stability of the tube is paramount in these applications to ensure smooth unwinding.
-
Construction: Heavy-duty, waxed cardboard tubes, often branded as Sonotubes®, are used as forms for pouring concrete columns and piers. Their strength allows them to hold the weight of wet concrete, and they can be easily stripped away after the concrete cures, making them a cost-effective alternative to permanent forms.
-
Textiles and Fabrics: Large-diameter tubes are used as cores for winding bolts of fabric, providing a stable spool for storage and transport in textile mills and retail environments.
-
Arts, Crafts, and DIY: Their accessibility and ease of use make cardboard tubes a popular material for creative projects, from building structures and organizers to use as molds for various materials.
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
From a sustainability perspective, cardboard tubes are an excellent choice. The majority are produced using recycled paperboard, reducing the demand for virgin timber and conserving natural resources. As a paper product, they are biodegradable and widely recyclable in standard paper recycling streams, helping to close the loop in the circular economy. This eco-friendly profile makes them an increasingly attractive option for businesses looking to reduce their environmental footprint.
In summary, the humble cardboard tube is a sophisticated engineered product. Its simple form belies its complex manufacturing process and its essential role in modern industry, packaging, and logistics.

 English
English Español
Español